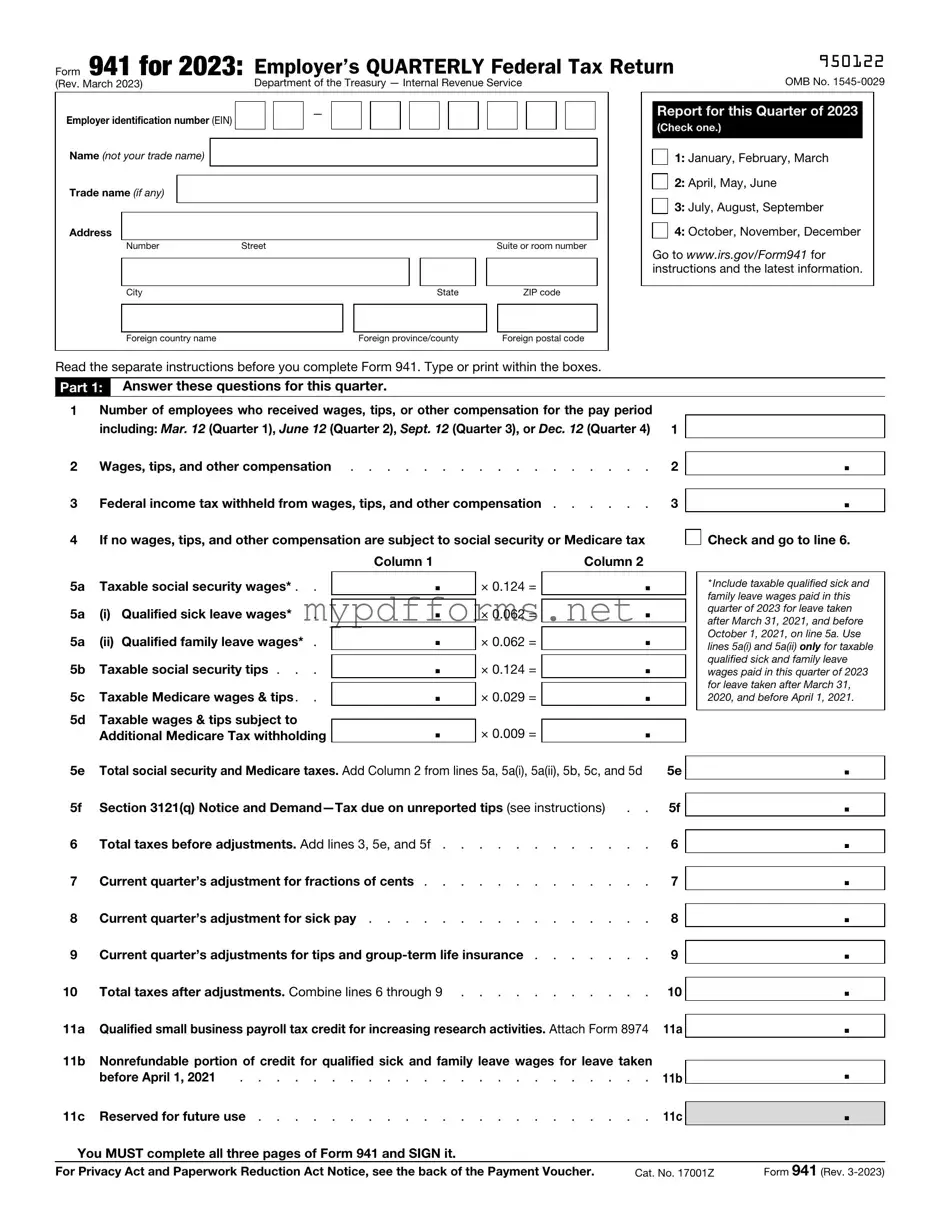
The IRS Form 940 is similar to Form 941 in that both are used by employers to report taxes related to employee wages. While Form 941 is filed quarterly and focuses on income, Social Security, and Medicare taxes, Form 940 is an annual report that specifically addresses the Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA). Employers use Form 940 to report and pay unemployment taxes, which help fund unemployment benefits for workers who lose their jobs. Both forms require accurate payroll information to ensure compliance with federal tax obligations.
Form W-2 is another document that shares similarities with Form 941. While Form 941 is filed quarterly, Form W-2 is an annual statement that employers provide to their employees. It reports the total wages paid to an employee and the taxes withheld throughout the year. Both forms are essential for tax reporting and ensure that employees have the necessary information to file their individual income tax returns. The data reported on Form W-2 is also derived from the payroll information that employers report on Form 941.
Form W-3 is closely related to Form W-2, serving as a summary of all W-2 forms issued by an employer. Like Form 941, which summarizes quarterly tax liabilities, Form W-3 consolidates the information from all W-2s into one document for submission to the Social Security Administration. Both forms are crucial for ensuring that the correct amounts of taxes are reported and that employees receive proper credit for their earnings and contributions toward Social Security and Medicare.
Form 943 is designed for agricultural employers, similar to Form 941. Both forms require employers to report taxes withheld from employee wages. However, Form 943 specifically pertains to farmworkers and includes unique provisions related to agricultural employment. The reporting periods align with those of Form 941, making it easier for agricultural employers to manage their tax obligations while ensuring compliance with federal tax laws.
Form 944 is another document that parallels Form 941, but it is intended for small employers with an annual payroll tax liability of $1,000 or less. Instead of filing quarterly, eligible employers can file Form 944 annually. This reduces the frequency of reporting for those with minimal payroll tax obligations while still ensuring that the IRS receives the necessary information about employee wages and tax withholdings.
Form 1099-MISC is a form used to report payments made to independent contractors and other non-employees. While Form 941 focuses on employee wages and taxes withheld, Form 1099-MISC serves a different purpose by documenting payments that are not subject to payroll taxes. Both forms are essential for accurate tax reporting, ensuring that the IRS has a complete picture of an employer's financial obligations and the payments made to various types of workers.
If you are looking to execute a property transfer, understanding the role of a Michigan Quitclaim Deed is crucial. This document facilitates the ownership shift without providing assurances regarding the title, making it ideal for personal transactions like those among family members or friends. For those interested in accessing a fillable form to ease the process, visit https://quitclaimdocs.com/fillable-michigan-quitclaim-deed.
Form 1040 is the individual income tax return that employees use to report their annual income, including wages reported on Form W-2. While Form 941 is a reporting tool for employers, Form 1040 is used by employees to calculate their tax liabilities. The information from Form 941 ultimately influences the amounts reported on Form 1040, as employees use the data to determine their eligibility for credits and deductions based on their reported income.
Finally, Form 1095-C is relevant for employers who provide health insurance to their employees. This form reports information about health coverage offered and is part of the Affordable Care Act requirements. While Form 941 deals with payroll taxes, both forms are essential for compliance with federal regulations. Employers must accurately report both payroll taxes and health coverage to avoid penalties and ensure that employees receive the necessary documentation for their tax filings.