Get IRS Schedule B 941 Form in PDF
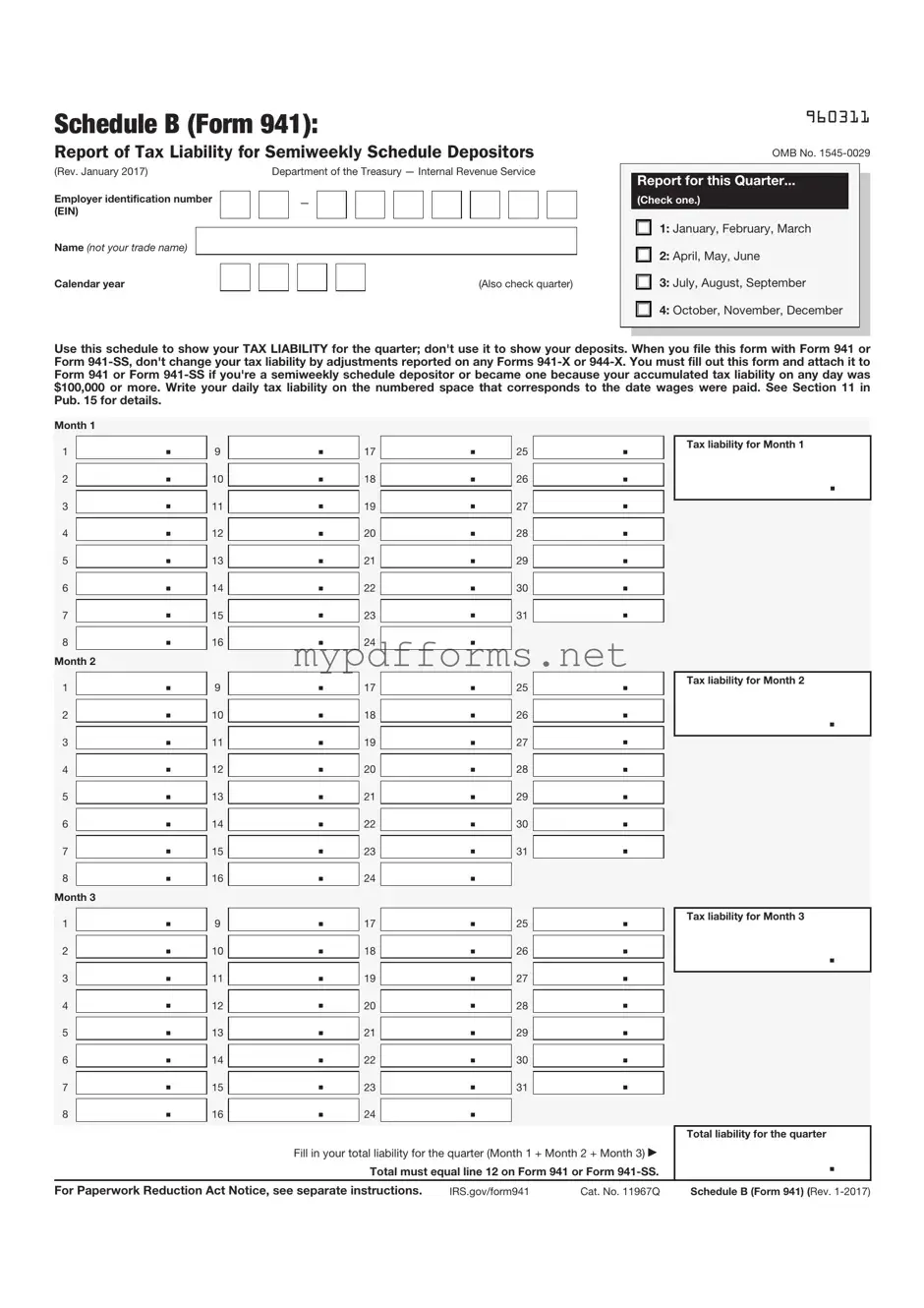
The IRS Schedule B (Form 941) is a crucial document used by employers to report their payroll tax liabilities and reconcile their tax payments. This form provides the IRS with information about the number of employees, wages paid, and taxes withheld during a specific quarter. Understanding how to accurately complete this form is essential for compliance and avoiding penalties.
Ready to fill out your Schedule B (Form 941)? Click the button below to get started!
Modify Document Here
Get IRS Schedule B 941 Form in PDF
Modify Document Here

Modify Document Here
or
⇓ PDF
Need to check this off quickly?
Edit and complete IRS Schedule B 941 online in just a few steps.